A circular economy seeks to eliminate waste by creating circular or closed-loop economic systems where materials are continuously reused. Unlike a traditional linear economy where products are manufactured, used and discarded, often ending up in a landfill, a circular economy envisions a reality where all products are durably designed, easily repaired and capable of being taken apart to their components for recycling and reuse.
What are the benefits of a circular economy?
Waste Reduction
Waste reduction is a major benefit of the circular economy. The circular economy’s goal is to reduce waste in all its forms, which keeps it out of landfills and the natural environment, thus creating cleaner and healthier ecosystems.
Circular economy practices focus on our current waste crisis, as well as how to eliminate waste entirely. This starts with product design and minimizing waste from the outset.
Resource Conservation
Another circular economy benefit is resource conservation. Circular production patterns decrease the need and production of new resources.
Emission Reduction
Product use and manufacturing contribute to roughly 45% of greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs). Materials management, including the production, consumption and disposal of materials, products and infrastructure, is a major share of GHGs.
Recycling and recirculating materials and products to extend their life cycles can help reduce emissions and improve circularity.
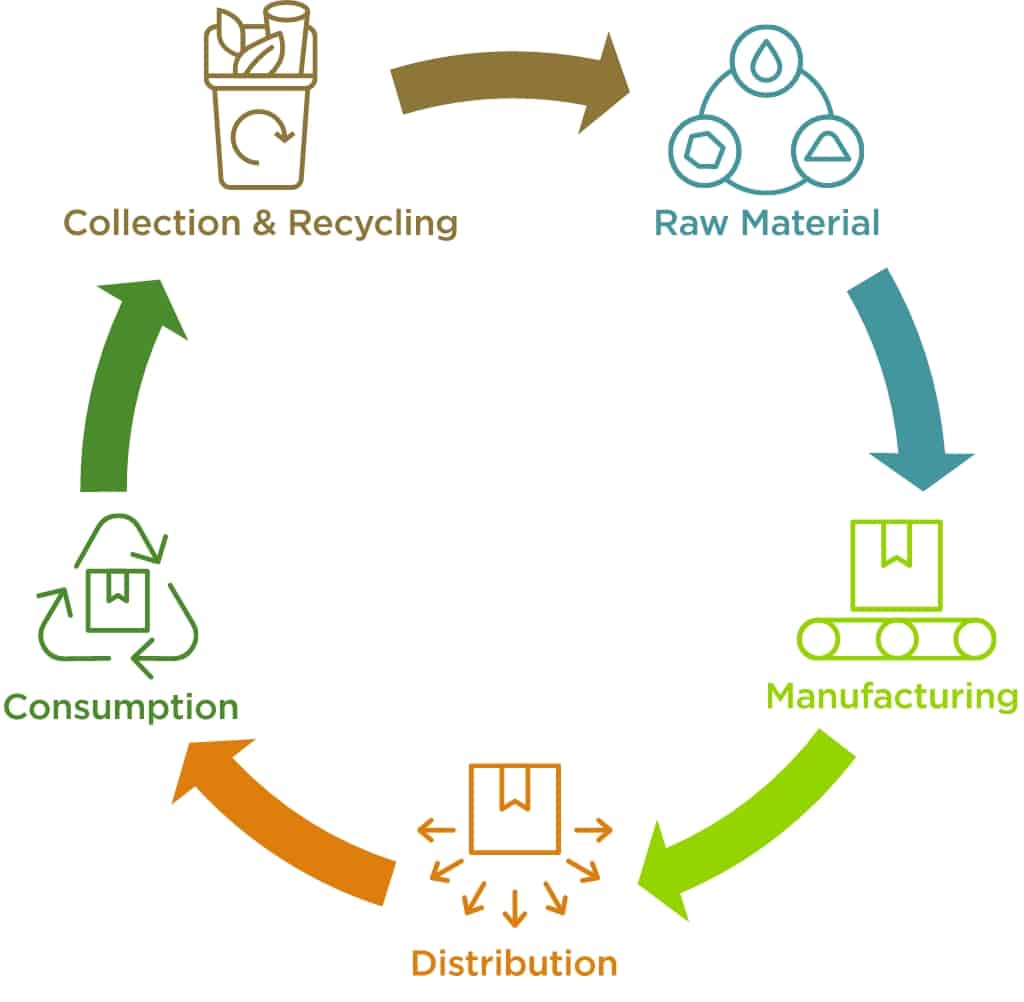
What is the circular economy’s role in waste management?
Circular economy practices challenge us to rethink landfilling as a waste management method and move toward solutions that reduce environmental pollution and emissions. A circular economy action plan takes what is considered waste and finds ways to turn it into valuable resources.
There are several ways to do this, including:
- Recycling materials for reuse in new product creation.
- Converting organic waste, or any biodegradable material that comes from plants or animals, into compost or livestock feed.
- Using a Waste to Energy process for hard-to-recycle items instead of putting them in a landfill.
- Tapping into methods such as chemical recycling to recover and transform materials such as breaking down plastics to their original properties.
The Influence of a Circular Economy Waste Management Approach
The components of the circular economy have influenced businesses and consumers to choose more environmentally friendly production and consumption patterns to reduce their environmental footprint. Businesses are investing in innovation, materials and technology to extend their products’ lifecycles and recyclability. Consumers are making more conscious choices about the products they buy.
The circular economy principles have also influenced policy related to waste and end of life management, including:
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) policies demand that businesses manage their products’ end of life and provide incentives for companies that design their products more sustainably.
- As an example, California’s SB 54 Plastic Pollution Prevention & Packaging Producer Responsibility Act, enacted in 2022, mandates that all packaging in the state be recyclable or compostable by 2032.
- The EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) requires businesses to disclose environmental impacts stemming from their operations, particularly emissions, with varying timelines for reporting directives based on company size and revenue.
- The EU’s Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) aims to double material circularity by 2030 and promotes the use of sustainable and circular products.
How does Federal International help with circular economy solutions?
With our roots in recycling dating back to our founding in 1914, Federal International has been committed to the principles of the circular economy from the beginning. We exemplify the circular economy in action with our business solutions and our own corporate sustainability strategy.
If your business needs to recycle its byproducts, such as cardboard, paper, plastic, metals or pallets, Federal Recycling provides tailored circular economy solutions that can meet your needs. Federal Recycling’s sole focus is recycling and brokering material for reuse to businesses in search of recycled raw materials for their manufacturing process.
If your business is required, or will be required, to source more end-of-life component materials, Federal Eco Foam and Federal Foam Technologies provide solutions for various industries. Federal Eco Foam recycles polyurethane foam from manufacturers and converters, as well as mattresses, furniture and seats to create recycled rebond foam. Rebond foam fulfills requirements for quality, durable and sustainable component materials, with the ability to be recycled to even a third life. FEF also engages in closed loop recycling by taking a manufacturer’s polyurethane scrap material and processing it into a form that can be reincorporated into their production process, as well as open loop recycling by processing and trading material to different industries, such as carpet underlay.
Federal Foam manufactures a diverse set of foam, plastic and composite materials, and when technical specifications allow, strategically sources sustainable materials for its customers, especially with plastics. FFT looks for open loop recycling opportunities and recycles its foam off throws to be recycled as a raw material in a new product. The company also applies the three R’s of recycling to packaging — reduce, reuse, recycle — which directly impacts packaging costs to customers but also indirectly impacts transportation emissions.
Our businesses touch every point of the circular economy upstream and downstream, and we continue to explore ways to do even more through new services and products, as well as intracompany collaboration to make our own processes more circular to reduce environmental impact.
With our unique, diverse business model and experience, we are uniquely positioned to help companies in their journey toward circular economy sustainability. Contact us to learn more about how our circular economy consulting, products and services can help contribute to your circular economy action plan by reducing your environmental footprint.






